10/19/2025
Obesity
Obesity is a non-communicable disease (NCD) and a problem that has become a global concern because of the many related pathologies, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, joint problems and mental health.
Preventing obesity is at the heart of the GIFA’s work for the Canton of Geneva and the Marchez, mangez malin! programme. Because breastfeeding is an important factor in the prevention strategy, both for the child and for the breastfeeding mother.
WHO facts en obesity
- In 2022, 1 in 8 people in the world were living with obesity.
- Worldwide adult obesity has more than doubled since 1990, and adolescent obesity has quadrupled.
- In 2022, 2.5 billion adults (18 years and older) were overweight. Of these, 890 million were living with obesity.
- In 2022, 43% of adults aged 18 years and over were overweight and 16% were living with obesity.
- In 2022, 37 million children under the age of 5 were overweight.
- Over 390 million children and adolescents aged 5–19 years were overweight in 2022, including 160 million who were living with obesity.
Source : https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
Breastfeeding – a preventive factor
COSI – Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative
Obesity (whether in children or adults) is multifactorial. Breastfeeding contributes in various ways to protecting the child (who is the future adult) but also the breastfeeding woman (see below).
It is important to emphasise the role of breastfeeding from the very start of nutrition, in order to lay the foundations for healthy metabolic regulation and balanced body weight. Overweight and obesity are often directly linked to the onset of diabetes 2, to the extent that we now talk of the ‘diabesity’ epidemic. The costs involved are considerable; in Switzerland, 10% of adults and 5% of children are affected: https://www.bag.admin.ch/bag/fr/home/gesund-leben/gesundheitsfoerderung-und-praevention/koerpergewicht/uebergewicht-und-adipositas/kosten-uebergewicht-und-adipositas.html
These are the figures for 2012. A new study is currently under way, with results expected towards the end of 2024.
- COSI Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative (or COSI) in Europe, the 6th survey takes place 2021-2023. https://www.who.int/europe/initiatives/who-european-childhood-obesity-surveillance-initiative-(cosi)
- COSI 2018-2020 https://www.who.int/europe/publications/i/item/WHO-EURO-2022-6594-46360-67071 The systematic collection and analysis of these data allows comparisons between countries and a better understanding of the progression of childhood overweight and obesity in Europe. Together, they clearly show that childhood obesity remains a major public health problem in the WHO European Region.
- COSI 2015-2017 Association between Characteristics at Birth, Breastfeeding and Obesity in 22 Countries: The WHO European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative – COSI 2015/2017 A World Health Organization (WHO) study of 16 countries across Europe has found that breastfeeding can cut the chances of a child becoming obese by up to 25%. In absolute terms, 16.8% of children who were never breastfed were obese, compared with 13.2% who had been breastfed at some time and 9.3% of children breastfed for six months or more.
Breastfeeding protects against Childhood obesity
Obesity (in children and adults) is multifactorial. Breastfeeding helps to protect the child (who is the future adult) in a number of ways.
It’s important to emphasise the role of breastfeeding from the very start of nutrition, to lay the foundations for healthy metabolic regulation and balanced body weight. Overweight and obesity are often directly linked to the onset of diabetes 2, to the point where we now speak of the ‘diabesity’ epidemic (a contraction of diabetes and obesity). The costs involved are considerable; in Switzerland, 10% of adults and 5% of children are affected: https://www.bag.admin.ch/bag/fr/home/gesund-leben/gesundheitsfoerderung-und-praevention/koerpergewicht/uebergewicht-und-adipositas/kosten-uebergewicht-und-adipositas.html
- Breastmilk (BM) is a physiological, bio-dynamic liquid that adapts to the child’s needs and retains its nutritional and immuno-protective values throughout the period of breastfeeding (even after 2 years)
- BM nourishes the baby’s microbiota and good bacteria
- BM provides hormones that regulate appetite and fat metabolism (ghrelin, leptin, adiponectin, apelin etc.).
- BM shapes children’s tastes through its variety and prepares them for diversification
- BM prepares them for the transition to the family table without necessarily using processed industrial foods.
Breastfeeding protects against Maternal obesity
Breastfeeding protects mother’s against obesity. See our dedicated page : woman’s health
References for breastfeeding and obesity
- 2022 Systematic review and meta-analysis of breastfeeding and later overweight or obesity expands on previous study for World Health Organization. Horta et al. Conclusion: L’allaitement réduit le risque de surpoids ou d’obésité, et il est peu probable que cette association soit due à un biais de publication ou à des facteurs de confusion résiduels.
- 2021 Zhang et al. Infant feeding and growth trajectories in early childhood: the application and comparison of two longitudinal modelling approaches. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34230577/ “Les résultats fournissent des preuves longitudinales solides pour encourager et soutenir l’allaitement prolongé dans le cadre de la prévention de l’obésité infantile.”
- 2021 Redsell et al. Barriers and enablers to caregivers’ responsive feeding behaviour: A systematic review to inform childhood obesity prevention. Conclusion : L’alimentation adaptée des nourrissons est un élément essentiel de la prévention de l’obésité infantile. Cette revue identifie les obstacles et les facteurs favorables à une alimentation adaptée aux besoins des soignants. Les résultats indiquent que la reconnaissance par les parents des signaux d’alimentation et de sécurité de l’enfant est essentielle au développement d’une alimentation adaptée, et qu’il est très important que les soignants et les nourrissons apprennent à se signaler les uns aux autres. Par conséquent, il est essentiel de fournir des informations et une formation en temps opportun pour soutenir les soignants.
- 2020 Zhang et al. Early Infant Feeding and BMI Trajectories in the First 5 Years of Life Conclusion: Longer breastfeeding duration was associated with lower BMIz (BMI relative to age) at age 5, supporting infant feeding guidelines that recommend prolonging breastfeeding duration for healthy growth.
- 019 Association between Characteristics at Birth, Breastfeeding and Obesity in 22 Countries: The WHO European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative – COSI 2015/2017 A World Health Organization (WHO) study of 16 countries across Europe has found that breastfeeding can cut the chances of a child becoming obese by up to 25%. In absolute terms, 16.8% of children who were never breastfed were obese, compared with 13.2% who had been breastfed at some time and 9.3% of children breastfed for six months or more.
- 2018 Azad et al. Infant Feeding and Weight Gain: Separating Breast Milk From Breastfeeding and Formula From Food Conclusion : L’allaitement est inversement associé à la vitesse de prise de poids et à l’IMC. Ces associations sont dépendantes de la dose, partiellement diminuées lorsque le lait maternel est donné au biberon, et considérablement affaiblies par la supplémentation en lait maternisé après la période néonatale.
- 2018 Mannan H. Early Infant Feeding of Formula or Solid Foods and Risk of Childhood Overweight or Obesity in a Socioeconomically Disadvantaged Region of Australia: A Longitudinal Cohort Analysis
- 017 Melnik et Schmitz Milk’s Role as an Epigenetic Regulator in Health and Disease. Citations : “Persistent uptake of bovine milk exosomal miRNAs may epigenetically enhance long-term orexigenic signaling promoting overgrowth and obesity of the human consumer of cow’s milk.” (page 14). “Taken together, cow’s milk transfers obesogenic and orexigenic miRNAs, predominantly miRNA-148a and miRNA-21, that maintain an epigenetic status that is intimately involved in the pathogenesis of diabesity.” (page 18)
- 2017 Wang L et al. Breastfeeding Reduces Childhood Obesity Risks Childhood Obesity, 2016, 13 (3), 197-204.
- 2017 Wallby T et al. Relationship Between Breastfeeding and Early Childhood Obesity: Results of a Prospective Longitudinal Study from Birth to 4 years Conclusion : La durée de l’allaitement pendant au moins 4 mois peut contribuer de manière indépendante à réduire le risque d’obésité infantile à l’âge de 4 ans.
- 2016 Victora C.G. et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet Breastfeeding Series Group. Lancet 2016, 387, 475–490. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26869575/
- 2014 Verduci et al. Epigenetic effects of human breast milk Citations : “This result may suggest both that breastfeeding may have beneficial effect on the obesity risk later in life in genetically predisposed groups.”- “Breastfed children may have lower risk of NEC, infectious diseases, later obesity, and related disorders,..”
- 2014 Vickers MH Early life nutrition, epigenetics and programming of later life disease. Nutrients. 2014 Jun 2;6(6):2165-78.
- 2014 Yan et al. The association between breastfeeding and childhood obesity: a meta-analysis. BMC Public Health, 14.
- 2014 Carling et al. Breastfeeding duration and weight gain trajectory in infancy. Conclusion : Infants at the highest risk for rising weight patterns appear to benefit the most from longer breastfeeding duration. Targeting mothers of high-risk infants for breastfeeding promotion and support may be protective against overweight and obesity during a critical window of development.
- 2013 Horta et Victora, Long-term effects of breastfeeding. A systematic review (WHO) Conclusion : The evidence suggests that breastfeeding may have a protective effect against type-2 diabetes, particularly among adolescents. Obesity/overweight seems to account for part of the association. Generalization from these findings is restricted by the small number of studies and the presence of significant heterogeneity among them. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/79198/9789241505307_eng.pdf?sequence=1
- 2012 Lillycrop KA et al. Epigenetic mechanisms linking early nutrition to long term health. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 26, 667–676. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22980048/
- 2012 Robinson S., Fall C.H. Infant Nutrition and Later Health: A Review of Current Evidence. Nutrients. 2012;4:859–874.
- 2012 Crume and Tabelea, Breastfeeding and Obesity: Impact on Women and Their Children https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-25023-1_18
- 2011 Moreno et al, Breastfeeding as Obesity Prevention “One important health benefit of breastfeeding is prevention of obesity. Obesity is one of the most serious health problems facing both children and adults today. Childhood obesity often leads to adult obesity, which causes many health problems including heart disease, diabetes, and even early death.” https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/1107563
- 2011 Lillycrop, K.A.; Burdge, G.C. Epigenetic changes in early life and future risk of obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 72–83.
- 2009 Stuebe A. The risks of not breastfeeding for mothers and infants. Rev. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009;2:222–231.
- 2004 Arenz, S. , Ruckerl, R. , Koletzko, B. , & von Kries, R. (2004). Breast‐feeding and childhood obesity‐a systematic review. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders, 28, 1247–1256. Nine studies with more than 69,000 participants met the inclusion criteria. The meta-analysis showed that breast-feeding reduced the risk of obesity in childhood significantly. Conclusion: Breast-feeding seems to have a small but consistent protective effect against obesity. Conclusion: Breast-feeding seems to have a small but consistent protective effect against obesity https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15314625
- 2000 Von Kries R, Koletzko B et al. Does breast-feeding protect against childhood obesity? Breast fed babies may have a high BMI, but are less overweight at age 5 years. The preventive effect of breast-feeding on overweight and obesity is an important additional argument for the promotion of breast-feeding in industrialised countries.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000;478:29-39. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11065058/
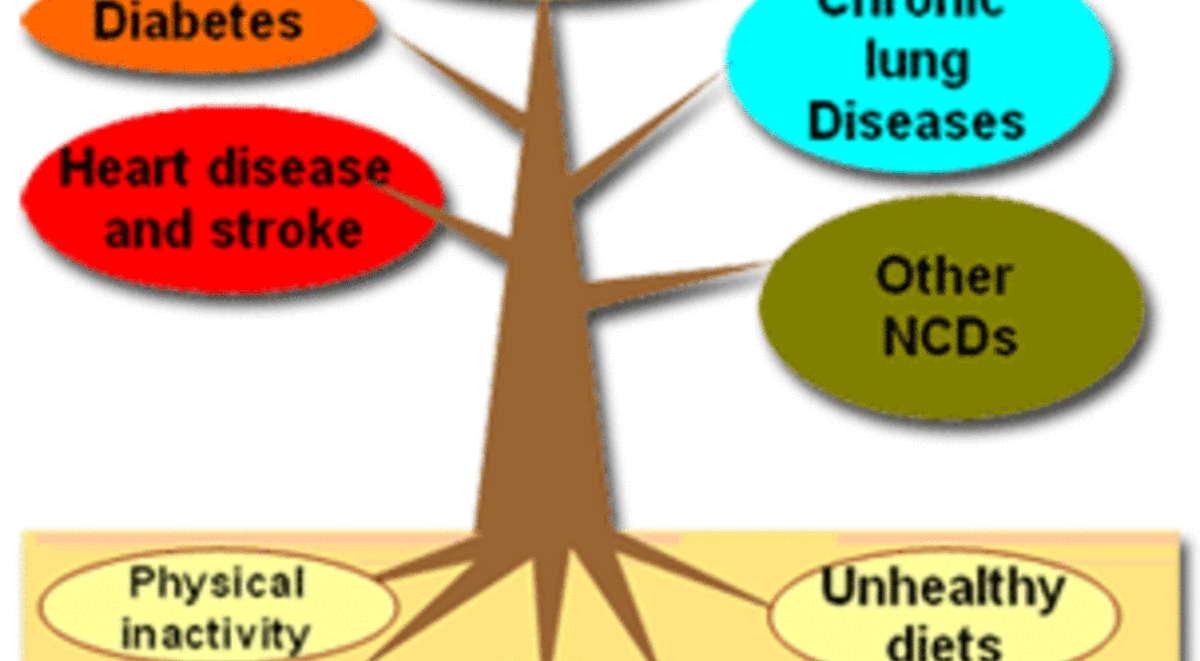
NCDs – a global public health issue
A non-communicable disease (or NCD for short) is a non-infectious disease that cannot be transmitted from person to person. Obesity, diabetes, cancer and cardiovascular disease are NCDs. In 2019, the World Health Assembly extended the WHO Global Action Plan on NCDs 2013-2020 until 2030. See the WHO page on key facts about https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases
Breastfeeding reduces risk factors for NCDs
An important way of combating NCDs is to focus on reducing the risk factors associated with these diseases. Certain behaviours, such as smoking, physical inactivity, poor diet and harmful use of alcohol, can be modified to reduce the risk of NCDs.
Encouraging breastfeeding also helps to reduce this risk, both for the health of the child and for the health of the mother. Breastfeeding is associated with normal body weight, normal insulin metabolism and good long-term physical and mental health. In other words, not breastfeeding is associated with obesity, diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, etc.
IBFAN statement on NCDs in 2023
At the World Health Assembly (WHA), IBFAN has supported WHO’s work on NCDs since the start, highlighting the need for Conflicts of Interest safeguards, clear terminology and the protection breastfeeding and sound child feeding – essential in preventing NCDs. FENSA (Framework of Engagement with Non-State Actors) has led to much confusion about identities and responsibilities. Corporations have no democratic accountability and health policies should be free of their influence. In our experience ‘multi-stakeholder’ partnerships with health-harming corporations delay effective legislation, especially on labels and marketing. WHO must develop a global definition for Ultra Processed products –not food and covered in claims about added micro-nutrients, yet do so much harm. Deaths from unhealthy food now exceed those of tobacco. We can say this because IBFAN is not a ‘stakeholder’ and has no financial ‘stake’ in this issue. See our page Conflict of interest
One important way of combating NCDs is to focus on reducing the risk factors associated with these diseases. Certain behaviours, such as smoking, physical inactivity unhealthy diet and the harmful use of alcohol, can be modified to reduce the risk of NCDs. Encouraging breastfeeding also helps to reduce this risk, for the health of both the child and the mother. Breastfeeding is associated with normal body weight, normal insulin metabolism, good physical and mental health, long-term physical and mental health. In other words
non-breastfeeding is associated with obesity, diabetes, cancer and cardiovascular disease etc.
NCDs and Covid-19
Breastfeeding is doubly important to protect against SARS-CoV2 as NCDs because
- NCDs are risk factors that aggravated a Covid-19 episode,
- breastmilk transmits many immunoprotective factors to the child. see also Immunology page
Benefits of breastfeeding
Breastfeeding is an indisputable fundamental value for the health of both mother and child. It’s also a guiding principle for prevention and health in Switzerland. It is therefore important to communicate in order to
- inform women, parents, employers and the medical profession about the benefits of breastfeeding,
- support women who choose to breastfeed, throughout the breastfeeding period,
- invest in training health professionals about breastfeeding,
- raise awareness among decision-makers of the need for support and information on breastfeeding,
- create a breastfeeding-friendly society.
We must bear in mind that breastfeeding is the foundation of public health and at the heart of prevention.
2016 The Lancet Breastfeeding Series states in its executive summary : “With a substantial development of research and findings for breastfeeding over the past three decades, we are now able to expand on the health benefits for both women and children across the globe. The two papers in this Series will describe past and current global trends of breastfeeding, its short and long-term health consequences for the mother and child, the impact of investment in breastfeeding, and the determinants of breastfeeding and the effectiveness of promotion interventions.”
Epigenetic impact
See our dedicated page Epigenetics.
Breastfeeding and women’s health
Breastfeeding is not just about feeding a child; important processes take place in the body of the breastfeeding woman that have a long-term positive influence on her health. See our dedicated page Woman’s health
Breastfeeding and infant health
Breast-feeding is the optimum nutrition for the health and the development of the child. See Infant’s Health and also Immunology page as well as The Lancet Breastfeeding Series 2023
